Composite Reinforced Geotextile — Manufacturer, High-Strength Solutions for Ground Stabilization
Engineered with fiberglass and warp-knitted polyester structures, reinforced geotextiles deliver exceptional tensile strength, dimensional stability, and crack-resistant performance for demanding civil and road projects.
Export Global
Factory Directly
Certified Quality
Main Types of Reinforced Woven Geotextile
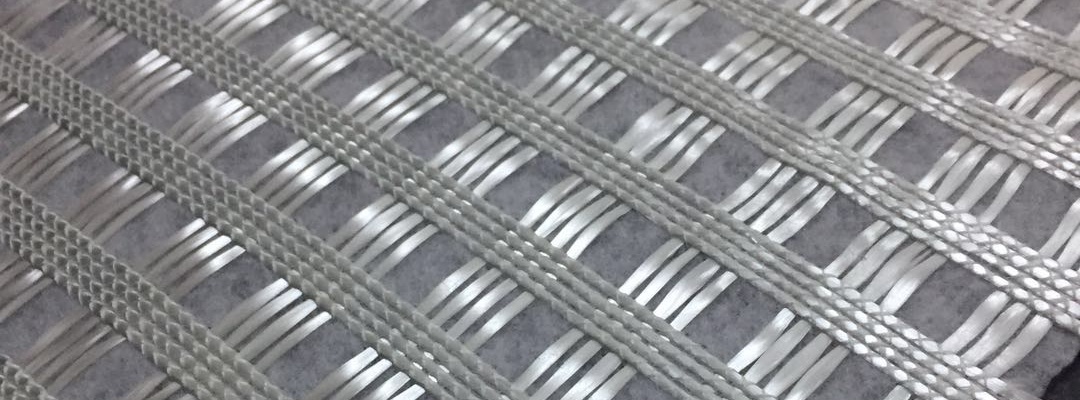

Warp-Knitted Reinforced Geotextile
Description
Warp-knitted reinforced geotextile is a composite material made by combining high-strength polyester yarns with nonwoven fabric through a warp-knitting binding process. During production, the binding yarn interlaces repeatedly through the warp, weft, and the fiber layer of the nonwoven geotextile, integrating them into a single composite.
This structure gives the material high tensile strength, low elongation, uniform deformation in both directions, excellent tear and abrasion resistance, high permeability, and strong filtration ability.
Key Features
- Straight and unbent yarn intersections distribute stress evenly.
- The binding yarn locks warp and weft firmly for stable load transfer.
- When subjected to tearing, fibers gather around the crack tip to enhance tear resistance.
- High strength, low creep, durable, and easy to install.
Specifications
- Width: 4–6 m (customizable)
- Strength: 35 kN/m – 300 kN/m (customizable)
- Function: Reinforcement · Drainage · Filtration · Separation · Protection
Applications
Used for coastal reclamation, river and dam reinforcement, slope retaining walls, soft soil improvement, and subgrade stabilization.
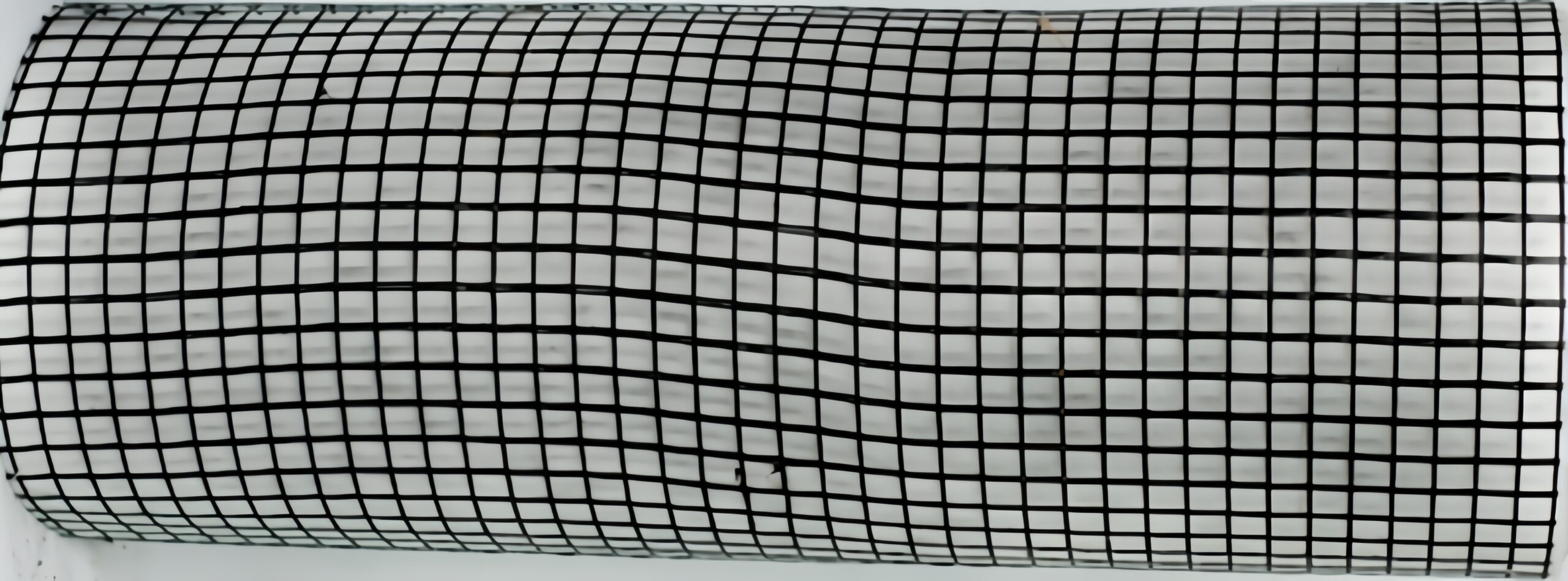
Fiberglass Reinforced Geotextile
Description
Fiberglass reinforced geotextile is made from glass fiber as the reinforcement material, laminated or bonded with short-fiber needle-punched nonwoven fabric. The fiberglass provides very high tensile strength and dimensional stability, while the fabric layer adds filtration and separation functions.
It differs from traditional woven fabric in that warp and weft yarns remain straight without bending at intersections. Binding yarns secure them firmly, distributing stress uniformly and increasing tear resistance.
Key Features
- High tensile strength with low elongation
- Balanced deformation in both directions
- Excellent tear and abrasion resistance
- High permeability and strong filtration capacity
- Long-term durability under heat, moisture, and mechanical stress
Specifications
- Width: 4–6 m (customizable)
- Weight: 400–1000 g/m² (customizable)
- Function: Reinforcement · Drainage · Filtration · Separation · Protection
Applications
Widely used in hydraulic engineering, municipal works, building foundations, transportation, metro and tunnel projects, and environmental protection fields. Typical uses include retaining walls, road slopes, reservoirs, coastal works, tunnels, landfill protection layers, and soft ground reinforcement.
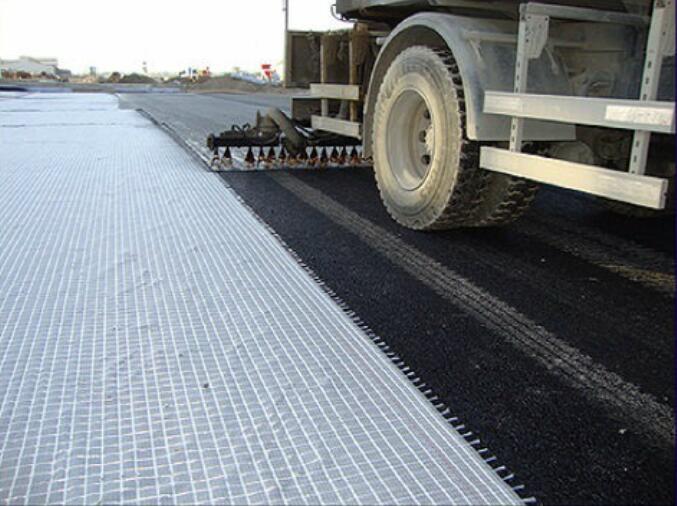

Reinforced Geotextile Installation & Quality Control (CQA)
Laying Methods
Surface Preparation:
Ensure the subgrade is smooth, compacted, and free of sharp stones or debris that may damage the fabric. Remove standing water before installation.
For reinforced geotextiles used on soft subgrades, apply a thin layer of sand or fine soil (5–10 cm) to create a uniform bedding surface.Placement:
Unroll the reinforced geotextile directly on the prepared surface in the designed alignment. Avoid dragging the rolls to prevent surface abrasion.
Make sure the warp (longitudinal) direction is aligned with the main stress direction of the structure (such as the slope line or embankment axis).Tensioning:
Keep the fabric moderately tensioned but not overstretched. Wrinkles or folds should be minimized to ensure full contact with the subgrade.
Jointing & Overlaps
Overlap Width:
Typical overlaps are 30–60 cm, depending on project requirements and fabric strength. For high-stress areas (e.g., slopes or subgrade joints), overlaps may be increased up to 1.0 m.Joining Method:
For warp-knitted reinforced geotextiles, use sewing or thermal bonding if specified.
For fiberglass reinforced types, overlaps are typically bonded with bitumen or adhesive spray during asphalt paving.
Ensure joints are staggered and not concentrated in a single line across the structure.
Anchoring & Fixing
Temporary Fixing:
Use sandbags, pins, or nails to prevent wind uplift before the next layer is placed. Fixing points should not damage the geotextile.Permanent Anchoring:
At slopes, embed the top edge into an anchor trench (minimum depth 0.3–0.5 m).
For road or pavement applications, ensure the geotextile remains firmly in place until the overlying material (soil, gravel, or asphalt) is installed.
Why Choose WP Specialist?
Over the years, WP Specialist has built a strong reputation as one of China’s trusted geotextile manufacturers and global suppliers of geosynthetic materials.
We focus on delivering reliable geotextile fabrics that meet the demanding needs of civil, road, and hydraulic engineering projects worldwide.
Our geotextiles combine high tensile strength, stability, and consistent quality — backed by factory-direct service and technical expertise.
- Free Samples of Geotextile Fabric
- Expert Project Support
- Reliable Quality Assurance
- Over 10 Years of Manufacturing Experience
- Factory Direct Supply
Ready to Specify a Geotextile?
- 15+ Years of Factory-Direct Expertise
- Custom-Engineered Solutions for Your Needs
- Global Shipping & Logistics Support
- A Transparent, No-Obligation Quote
- 100% Confdentiality Guaranteed
Your email information will be kept strictly confdential and our business staff will ensurethat your private information is absolutely safe!
Contact
- info@waterproofspecialist.com
Reply within 12 hours!
Please pay attention to the email with the suffix “@waterproofspecialist.com”.


