Concerned about pollutants contaminating groundwater sources? A single leak from a landfill or waste pond can lead to environmental disaster and huge cleanup costs, jeopardizing your project and reputation.
A geomembrane protects groundwater by acting as a physical, impermeable barrier that isolates contaminants like landfill leachate or industrial waste from the subsoil. It is welded into a continuous sheet, preventing pollutants from seeping downward into aquifers and ensuring long-term environmental containment.
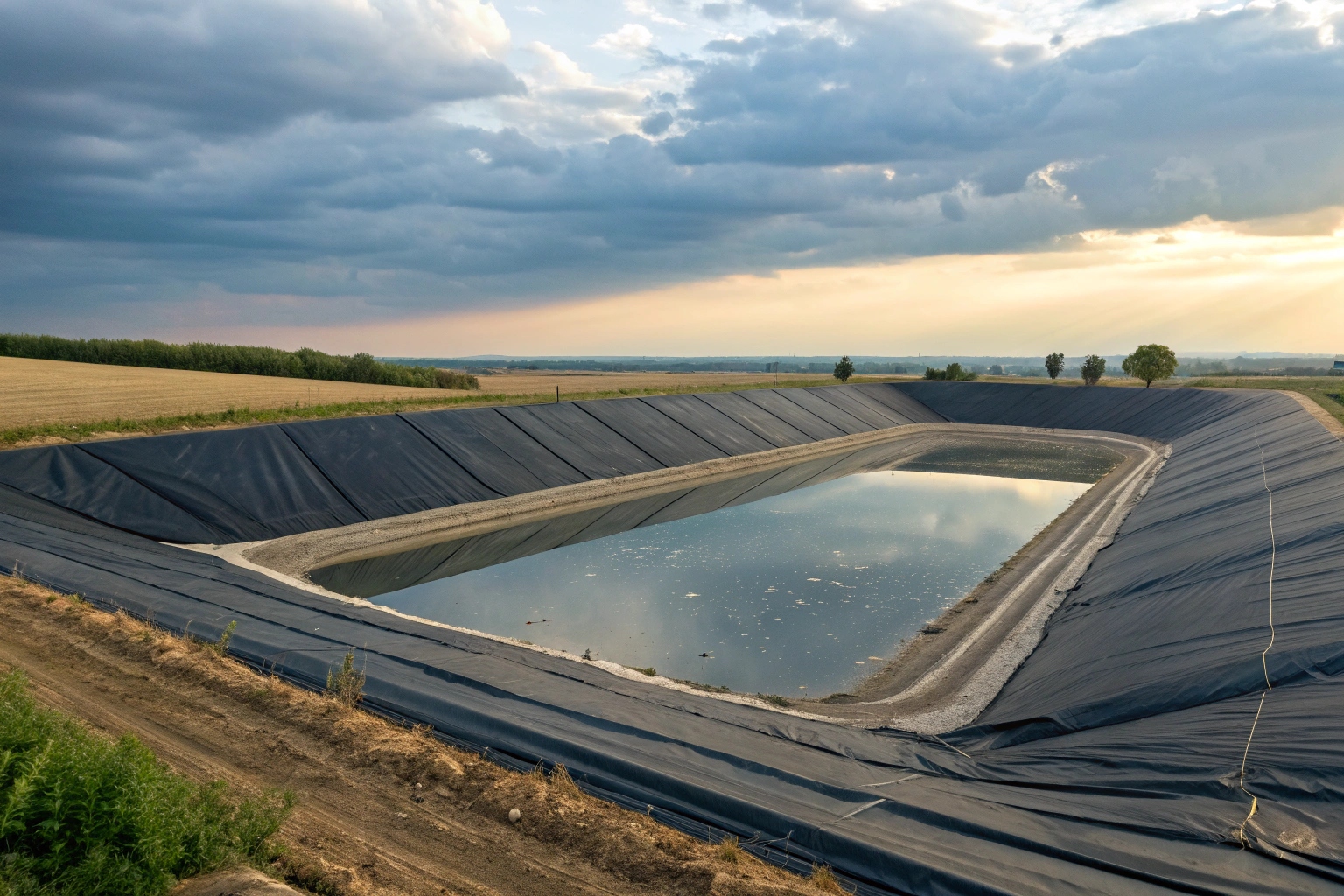

This engineered solution is not just a simple plastic sheet; it is the core component of a modern containment system. Its ability to protect our most vital water resources relies on a combination of specific material properties, proven applications, and most importantly, quality-controlled installation. Understanding how these factors work together is critical for any engineer or project manager tasked with ensuring environmental safety.
How does geomembrane act as a barrier against pollutants and leachate?
It's natural to question how a relatively thin membrane can reliably contain tons of hazardous waste. If it's just a sheet, what stops leaks from happening, especially in a complex system?
A geomembrane acts as the primary barrier by physically separating the waste from the soil. In modern systems, it works with drainage layers and secondary liners (like GCLs) to create a redundant, high-security system that can detect and collect leaks before they cause harm.
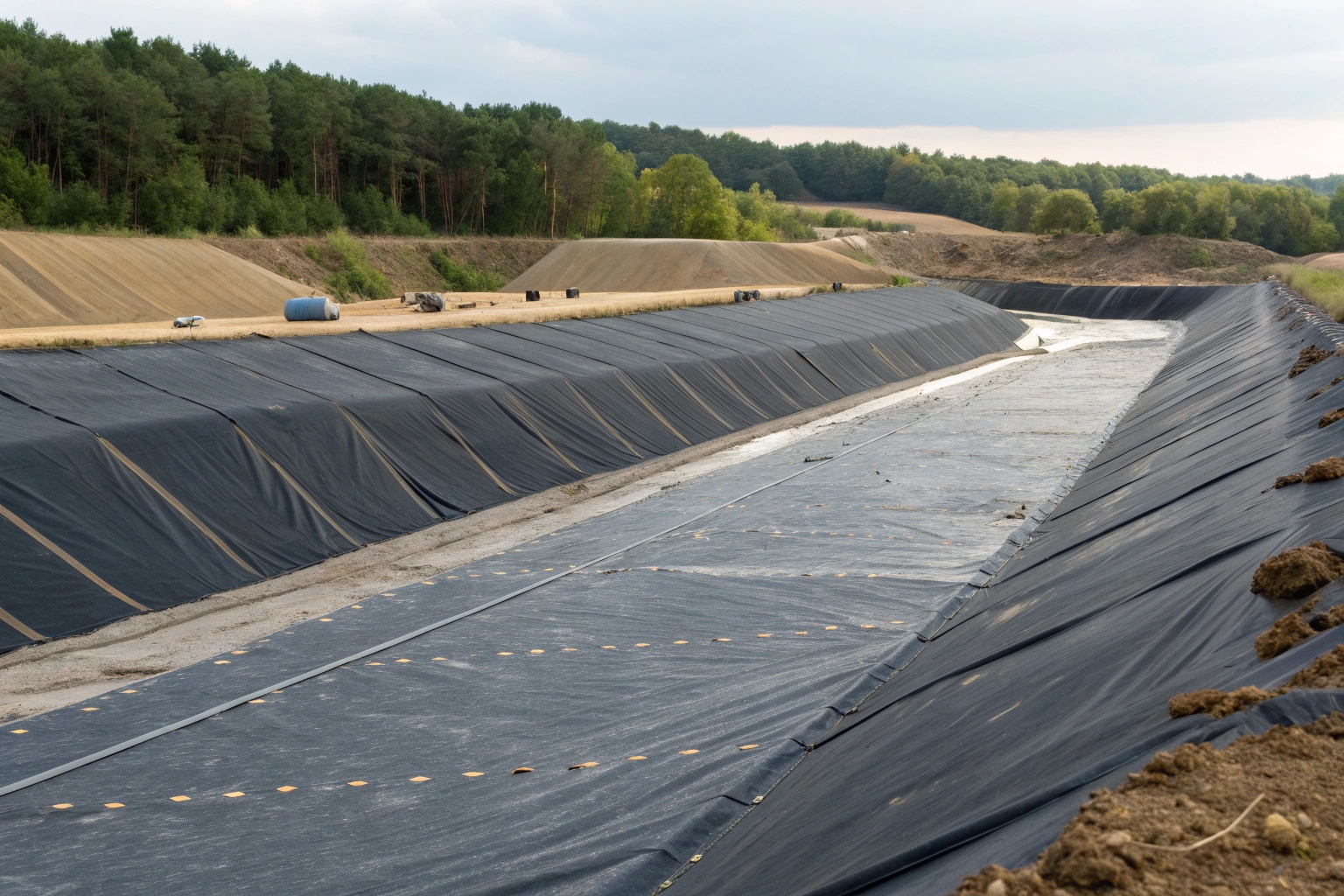

This multi-layered approach is the key to its effectiveness. The geomembrane provides the main impermeable shield, while other geosynthetic components add layers of safety and control.
Components of a Modern Containment System
- Primary Geomembrane: The main impermeable barrier that is in direct contact with the waste.
- Leachate Collection Layer: A geonet or gravel layer above the primary liner to collect and remove contaminated liquids.
- Revestimiento de arcilla geosintética (GCL): Often used as a secondary barrier beneath the geomembrane, providing a self-healing layer of protection.
- Leak Detection System: A drainage layer between the primary and secondary liners that collects any potential leaks, allowing for rapid detection and response before the environment is impacted.
This composite design creates a robust, multi-barrier system that provides unparalleled protection for groundwater.
What material properties make geomembrane effective for groundwater protection?
Choosing a liner based on price alone is a huge mistake. A low-quality material will degrade and fail under exposure to chemicals and sunlight, compromising your entire project and its environmental objectives.
Key properties are extremely low hydraulic conductivity (near zero permeability), high chemical resistance to harsh leachates, and long-term durability against UV radiation and physical stress. These ensure the barrier remains intact for its entire design life, preventing pollutant migration.
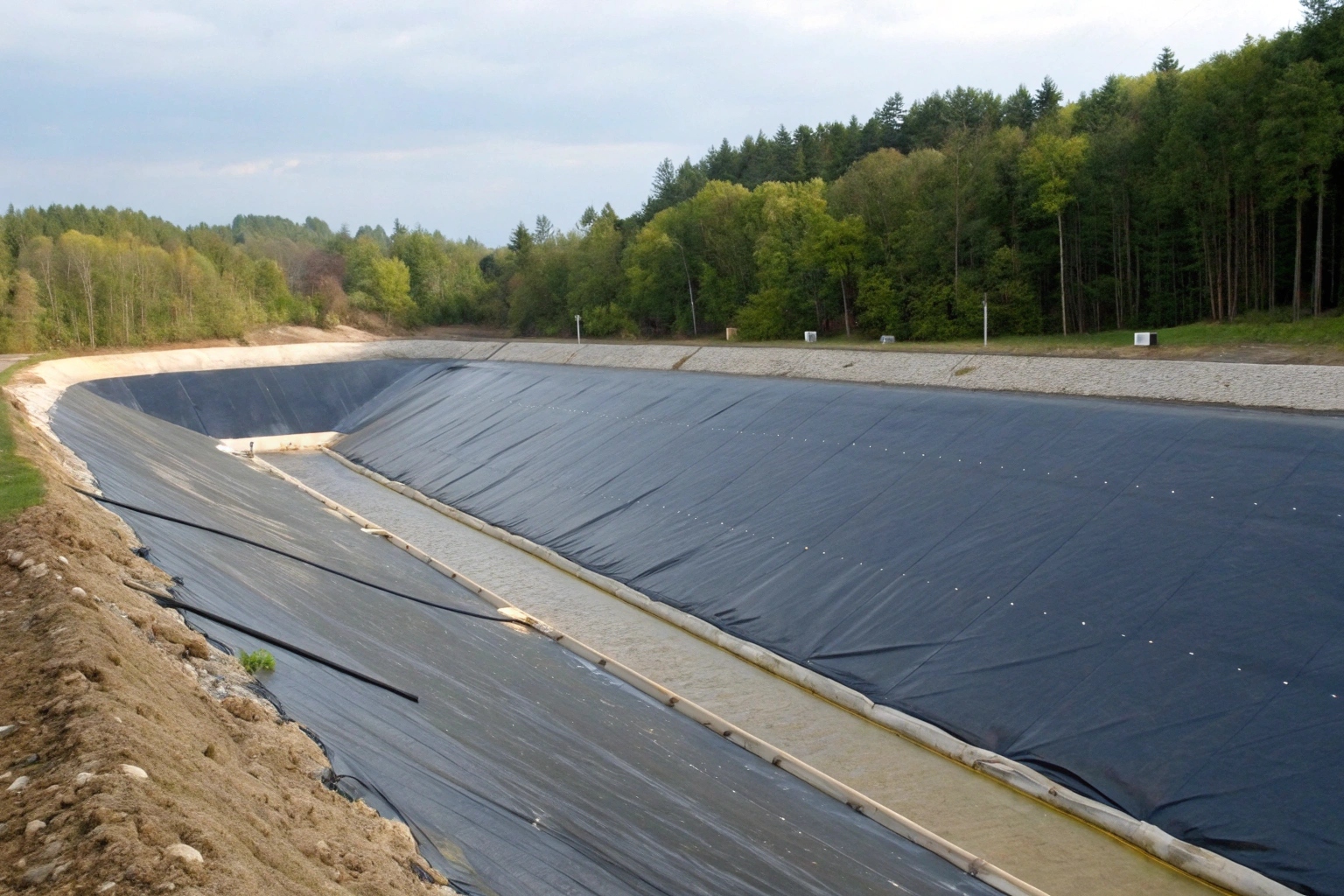

A geomembrane's performance is defined by verifiable, engineered properties. These are not just marketing claims; they are measurable standards that ensure the liner can withstand the demanding conditions of a containment facility.
Essential Performance Properties:
- Low Permeability: With a hydraulic conductivity as low as 10⁻¹⁶ cm/s, the material is practically impermeable, forming a tight seal against liquids.
- Chemical Resistance: High-quality resins (like HDPE) are formulated to be inert to a wide range of aggressive chemicals, acids, and bases found in industrial waste and landfill leachate.
- Durability: Additives like carbon black (minimum 2%) provide excellent UV resistance, while antioxidants prevent thermal degradation. The material must also have high tensile and puncture strength to resist installation and operational stresses.
Where is geomembrane used to prevent groundwater contamination in engineering projects?
Understanding the science is one thing, but where does this liner really make a difference? Applying it in the wrong context is a waste, but in the right one, it's an indispensable environmental tool.
Geomembranes are used in any project requiring contaminant isolation. Key applications include municipal solid waste landfills, mining heap leach pads, hazardous waste containment cells, wastewater treatment lagoons, and secondary containment for oil and gas facilities to prevent pollutants from reaching groundwater.
These projects all share a common, non-negotiable requirement: the potentially harmful liquids they manage must be permanently isolated from the surrounding environment, especially from underlying aquifers.
Critical Applications:
- Landfills: They form the base liner and final cap systems, preventing toxic leachate from escaping into the soil and groundwater.
- Mining: Used for heap leach pads to contain chemical solutions (e.g., cyanide) used in mineral extraction, and for tailings dams to secure processing waste.
- Wastewater Ponds: Line municipal and industrial lagoons to prevent contaminated water from seeping into the ground.
- Secondary Containment: Provide a failsafe barrier around fuel tanks, chemical storage areas, and oil facilities to contain spills.
How can I ensure long-term groundwater safety with proper geomembrane selection and installation?
Even the best geomembrane will fail if installed poorly. A single puncture or a bad weld during installation can create a leak path that compromises the entire containment system and your investment.
Ensure safety by selecting a geomembrane that meets industry standards (e.g., GRI-GM13) and demanding Manufacturer's Quality Control reports. On-site, enforce a strict Construction Quality Assurance (CQA) plan that includes rigorous subgrade preparation and seam testing to eliminate defects.
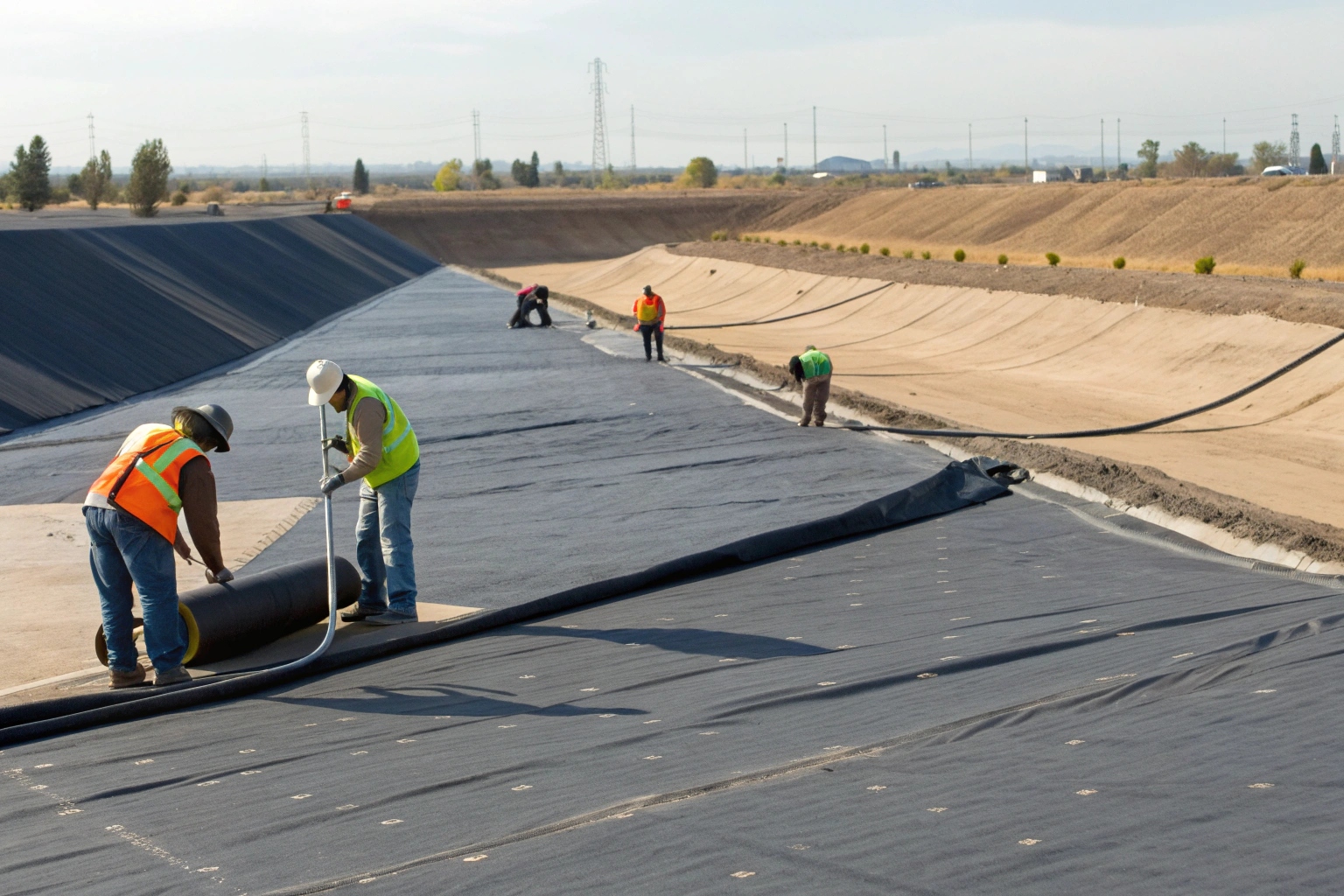

Long-term success is a direct result of two factors: choosing the right material and installing it perfectly. There is no room for error in either step.
Key Steps for Assuring Groundwater Safety:
- Material Verification: Always source from a reputable manufacturer. Review the Technical Data Sheet to ensure it meets project specs and request the MQC certificate for your specific batch to verify it was tested and passed.
- Subgrade Preparation: The ground beneath the liner must be smooth, compacted, and free of sharp objects that could cause a puncture. A protective nonwoven geotextile is often installed first as a cushion.
- Expert Installation & CQA: Use certified welding technicians. Every seam must be non-destructively tested (e.g., air pressure test for dual seams, vacuum box for single seams) to confirm its integrity. A final electrical leak location survey is often performed on the completed liner to find any pinholes before it is covered.
Conclusión
A geomembrane protects groundwater by providing a durable, impermeable, and verifiable barrier. Proper material selection, paired with certified, quality-controlled installation, is essential to ensure long-term environmental safety and project success.





