Choosing the wrong welding machine leads to weak seams and catastrophic leaks. Project delays and costly repairs are risks you can't afford, all because of an improper equipment choice.
The three primary types are hot wedge welders for long, automated seams on HDPE; hot air welders for details and PVC liners; and extrusion welders for repairs and thick connections. The right choice depends on your liner material, project scale, and application type.
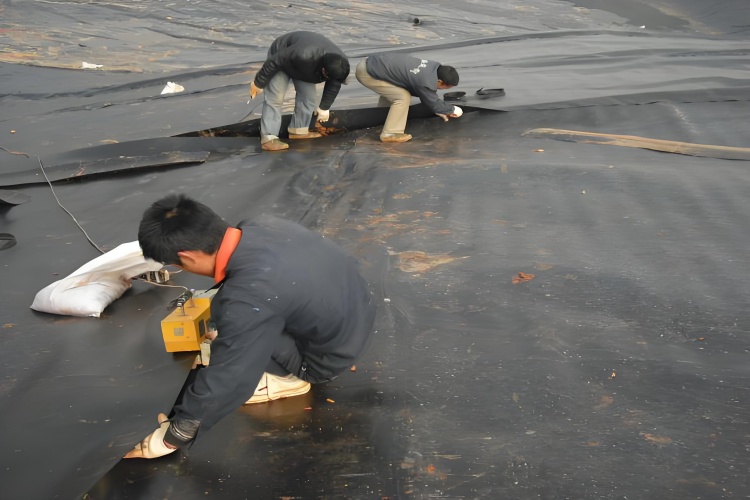

While these three machines cover most applications, understanding the specific strengths and limitations of each is critical for ensuring a durable, leak-proof installation. A machine that is perfect for a large, flat reservoir liner will be completely unsuitable for detailed pipe penetration work. Let's break down the equipment so you can make an informed decision for your next project.
What types of geomembrane welding machines are commonly used for HDPE liners?
Using the wrong welder on thick HDPE can result in a cold, weak bond. This material demands high, sustained heat and pressure to create a reliable seam, and not all machines can deliver.
For HDPE liners, hot wedge welders are the primary workhorse for long, straight seams, while extrusion welders are essential for repairs, patches, and connecting the liner to structures. These two machines are specifically designed to handle the high temperatures and pressures HDPE requires.
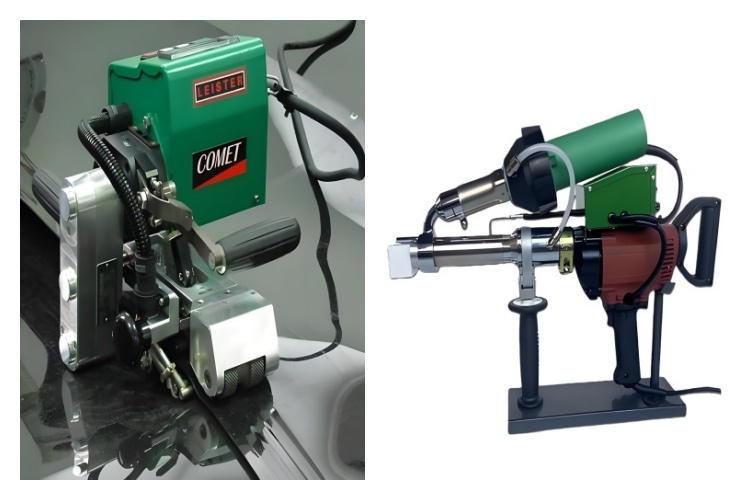

HDPE's semi-crystalline structure requires a specific combination of heat and pressure to achieve a proper molecular fusion. Here’s why these tools are the industry standard:
[Hot Wedge Welders
These are self-propelled machines that travel along the seam overlap. A heated metal wedge melts the two liner surfaces, and pressure rollers immediately press them together, creating a consistent, strong bond. They produce a double seam with a central air channel, which allows for on-site pressure testing to verify the weld's integrity—a critical quality assurance step.
Extrusion Welders
This handheld tool functions like a heavy-duty glue gun. It takes a solid polymer rod (of the same material as the liner), melts it, and extrudes a thick bead of molten plastic directly onto the seam or patch area. This method is slower but creates an incredibly strong, thick weld, perfect for patching holes, welding around pipes, and terminating the liner at concrete structures.
How do I decide which geomembrane welder fits my project requirements and materials?
Buying a welder based on price alone can be a costly mistake. An expensive machine might be overkill for your needs, while a cheap one could fail to produce certifiable seams, jeopardizing the entire project.
To choose the right welder, first match the machine to your material (HDPE/LLDPE vs. PVC/TPO). Then, assess your project's geography—large, open areas require a hot wedge welder, while complex details demand handheld hot air or extrusion welders.
Your decision should be a logical process based on three core factors: the material you are welding, the type of work you are doing, and the scale of your project.
1. Match the Welder to the Geomembrane
The polymer type dictates the required temperature and welding method.
- HDPE & LLDPE: Require high heat and pressure. The best choices are hot wedge for main seams and extrusion for details.
- PVC, TPO, & FPO: These more flexible materials melt at lower temperatures. A hot air welder is often the preferred tool, especially for detail work, as its focused heat is effective and easy to control.
2. Match the Tool to the Task
Different areas of an installation require different tools.
- Long, Straight Field Seams: A hot wedge welder provides unmatched speed and consistency.
- Detailed Work & Corners: Welding around pipes, sumps, and sharp corners is impossible for a wedge welder. This is where a hot air welder provides the necessary flexibility.
- Repairs & Patches: An extrusion welder is the best choice for filling holes or applying patches due to the thick, robust weld it produces.
What key factors affect the cost and efficiency of a geomembrane welding machine?
Focusing only on the purchase price ignores the true cost of ownership. Factors like welding speed, operator skill, and maintenance needs can have a much larger impact on your project's budget and timeline.
Efficiency is driven by welding speed and automation, where hot wedge welders excel. Cost is influenced by the machine's complexity, power, and features like digital controls and data logging. A welder with precise controls may cost more but reduces waste and operator error.
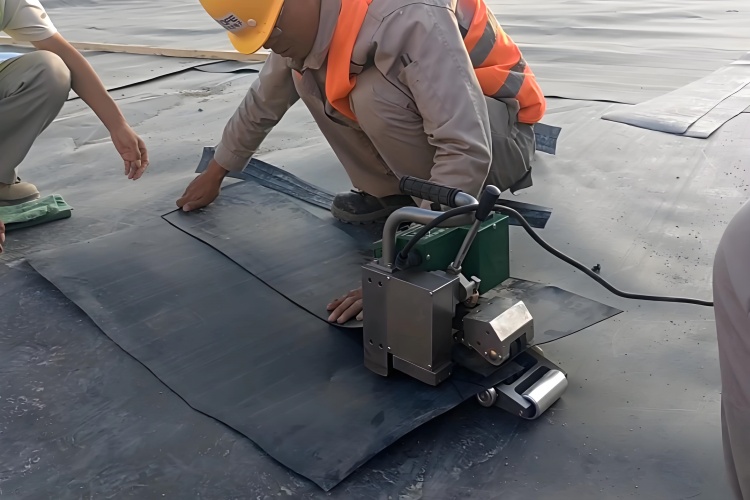

When evaluating the total cost and performance, consider these trade-offs:
- Speed vs. Strength: Hot wedge welders are the fastest for long seams, making them highly efficient for large projects like landfills or reservoirs. Extrusion welders are the slowest but produce the strongest, thickest welds, making them efficient for critical repairs where speed is secondary to security.
- Automation vs. Flexibility: Automated, self-propelled wedge welders ensure high consistency and reduce operator fatigue, boosting efficiency on large, flat sites. Handheld hot air guns are less efficient for large areas but offer essential flexibility for custom work.
- Initial Cost vs. Operating Cost]: A basic machine may have a low purchase price, but if it lacks precise temperature and speed control, it can lead to failed seams, wasted material, and costly rework. A higher-end machine with digital controls provides better quality assurance, saving money in the long run.
How can I ensure the welding equipment I choose is reliable and meets long-term performance standards?
A welder that constantly breaks down or produces inconsistent seams is a liability. On-site equipment failure halts progress, costs money, and damages your reputation for quality work.
Ensure reliability by choosing welders from reputable manufacturers with proven field performance. Look for features like robust construction, high-quality heating elements, strong drive motors, and readily available spare parts. Prioritize machines that offer precise, repeatable digital controls for consistent results.
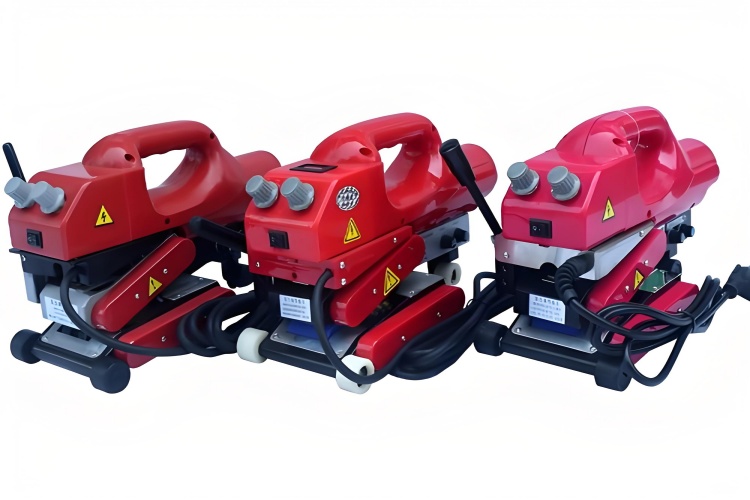

Long-term value comes from durability and consistent performance. Here is what to look for when sourcing your equipment:
Key Features for Reliability
- Digital Controls: Machines with digital displays for temperature, speed, and pressure allow operators to set and maintain precise parameters, ensuring every foot of weld meets project specifications. This is superior to analog dials, which can be less accurate.
- Build Quality: Look for a sturdy frame, durable motors, and high-quality electronic components that can withstand the harsh conditions of a construction site.
- Serviceability: Choose a brand that offers easy access to common replacement parts like heating elements, pressure rollers, and carbon brushes. A machine that is easy to maintain and repair in the field will have a much longer service life.
- Quality Assurance Features: For hot wedge welders, the ability to create a testable air channel is a non-negotiable feature for most professional-grade projects. Some advanced models also offer data logging to record welding parameters for quality control reports.
Conclusion
Choose a hot wedge welder for large HDPE projects, a hot air welder for details and flexible liners, and an extrusion welder for repairs. Match your machine to your material and project needs.





