Biaxial Geogrid— Manufacturer, Specifications & Ground Reinforcement Solutions
Designed for soil stabilization and base reinforcement, biaxial geogrids provide balanced tensile strength in both directions — perfect for highways, parking lots, and embankments. Reliable quality, delivered from our factory.
Uitvoer Global
Fabriek direk
Certified Quality
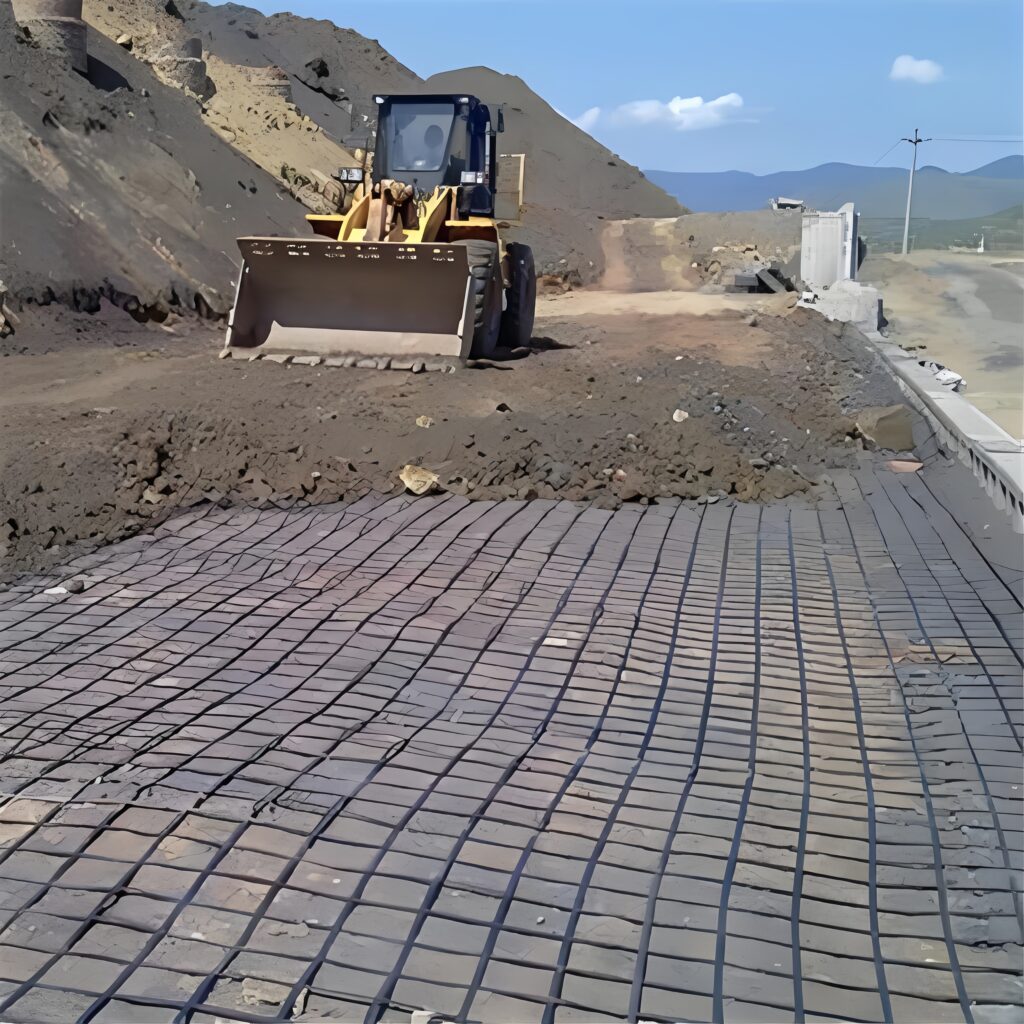

Special Properties of Tweeassige Geogrid
The biaxial design provides balanced reinforcement along both the longitudinal and transverse axes, effectively distributing loads and improving subgrade bearing capacity.
The grid’s interlocking structure forms a stable load-transfer system within the soil, preventing lateral spreading and deformation of road bases or embankments.
With the addition of carbon black and anti-aging stabilizers, the material resists acids, alkalis, corrosion, and long-term UV degradation.
Even under sustained load, the geogrid maintains its geometry, ensuring long-term performance in permanent foundations and pavements.
Suitable for reinforcing roads, railways, airports, docks, retaining walls, slopes, and mining sites, providing lasting structural stability.
Leer Ken Tweeassige Geogrid
A biaxial geogrid is a polymer reinforcement mesh made from polypropylene (PP) or high-density polyethylene (HDPE) that is stretched in both longitudinal and transverse directions.
This two-way tensile structure improves soil strength, distributes loads evenly, and stabilizes subgrades in roads, railways, and embankments.
The main purpose of a biaxial geogrid is to reinforce and stabilize the ground.
It increases the bearing capacity of soil, prevents rutting and deformation, and extends the service life of pavements, embankments, and parking areas by creating a strong interlock between the grid and the soil particles.
Biaxial geogrids are mainly classified by material composition and manufacturing process.
The most common type is the plastic biaxial geogrid, made from polypropylene (PP) or high-density polyethylene (HDPE) through a two-way stretching process.
Other geogrid materials — such as steel-plastic, fiberglass, of polyester composite geogrids — can also be manufactured in bidirectional forms, but they belong to different categories due to their distinct reinforcement mechanisms and material structures.
In practical use:
Plastic biaxial geogrid → for roads, foundations, and embankments.
Steel-plastic geogrid → for high-load retaining structures.
Fiberglass or polyester geogrid → for asphalt reinforcement and pavement stabilization.
Triaxial geogrid → advanced type with three-directional load distribution.
A uniaxial geogrid provides strength mainly in one direction (longitudinal), making it ideal for retaining walls and slopes.
A biaxial geogrid offers equal strength in both longitudinal and transverse directions, distributing stress more evenly — best for roads, foundations, and large-area soil stabilization.
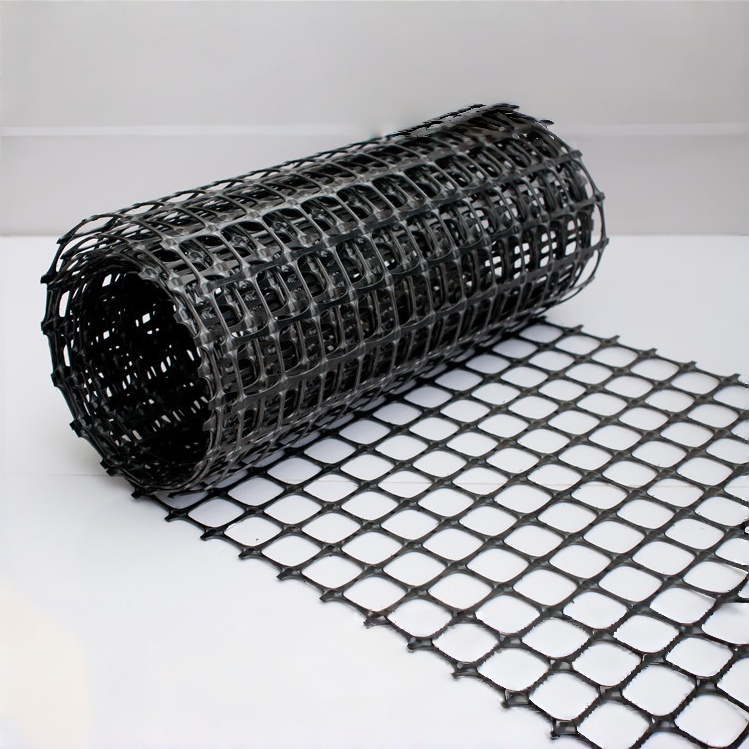

Upgraded Versions:Triaxial & Multiaxial Geogrid
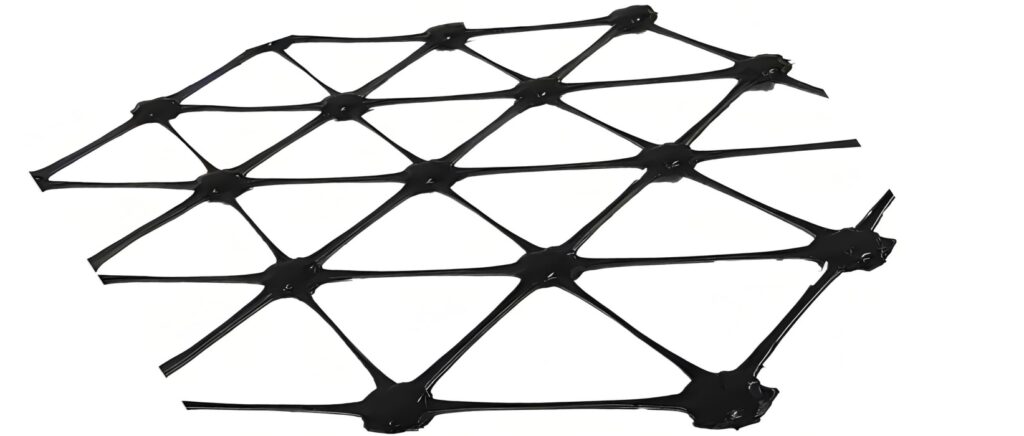
Tweeassige Geogrid
Triaxial geogrid is an upgraded version of the traditional biaxial type, featuring a triangular (three-directional) structure instead of square apertures.
This design distributes loads more evenly in multiple directions, improving shear resistance and stability under complex stress conditions.
It is widely used for highways, airports, container yards, and heavy-duty platforms where traffic loading comes from various angles.
Key Benefits:
Three-direction tensile reinforcement for multi-axial stability
Higher stiffness and better interlock with aggregates
Excellent resistance to deformation and rutting
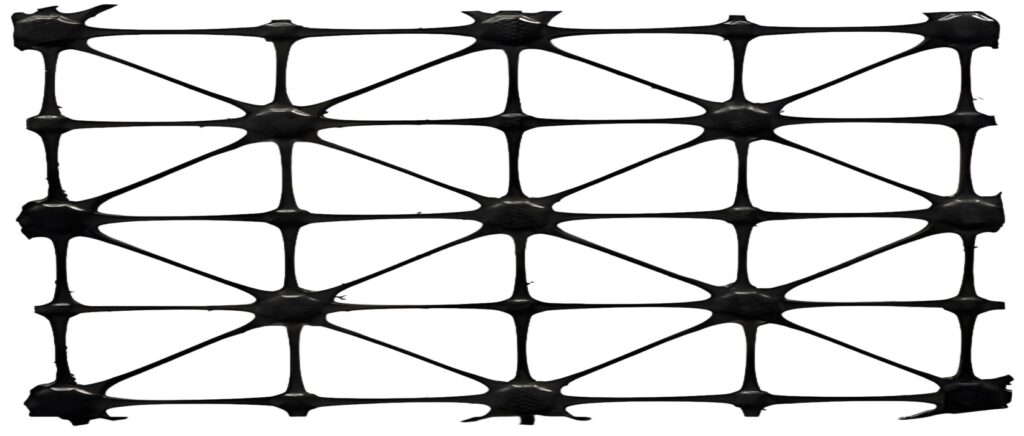

Multiaxial Geogrid
Multiaxial geogrid extends the concept further, using four or more tensile directions to achieve uniform performance in any loading orientation.
It combines the flexibility of polymer materials with a multi-direction mesh pattern, making it suitable for weak subgrades, high-traffic pavements, and geotechnical structures requiring long-term settlement control.
Key Benefits:
Multi-directional tensile structure for ultimate stability
Improved stress diffusion in soft or unstable soils
Enhanced bearing capacity and reduced surface deformation
Uniaxial vs Biaxial vs Triaxial (Multiaxial) Geogrid: Key Differences & Engineering Applications
Uniaxial, biaxial and triaxial geogrids are polymer reinforcement meshes used to enhance soil stability and bearing capacity. They differ mainly in tensile direction, load distribution en structural stiffness. Use the comparison below to choose the right type for your project.
| Comparison Aspect | Eenassige Geogrid | Tweeassige Geogrid | Triaxial / Multiaxial Geogrid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material & Structure | Extruded polymer sheet (PP/HDPE) that is stretched in one direction; apertures typically rectangular. | Extruded polymer sheet (PP/HDPE) that is stretched longitudinally and transversely; apertures square/rectangular. | Advanced mesh with triangular or multi-directional geometry; multi-axis molecular orientation for uniform behavior. |
| Tensile Direction & Stiffness | Single-direction tensile strength and high stiffness along the machine direction. | Two-direction balanced tensile strength; good in-plane stiffness for large areas. | Three or more directions; highest isotropic stiffness and confinement of aggregates. |
| Typical Tensile Strength (kN/m) | 30–200 (grade dependent; high values for walls/slopes). | 15–60 (common grades such as 15/15 to 50/50). | 30–80 (varies by design and manufacturer). |
| Load Distribution & Rutting Control | Excellent resisting outward movement in one direction; ideal for reinforced earth structures. | Distributes traffic loads evenly in two axes; reduces differential settlement and rutting. | Best for multi-directional traffic; superior shear resistance and deformation control. |
| Creep / Long-Term Performance | Very good along the primary axis; stable for long-term retaining structures. | Good bi-directional stability under repeated loading; low creep at service strain. | Highest resistance to deformation under complex stress paths; designed for heavy-duty, long-life pavements. |
| Chemical & Weather Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids/alkalis and weathering (with carbon black/UV stabilizers). | Excellent; comparable to uniaxial. Suitable for a wide range of soils. | Excellent; often specified where harsh environments and long design life are required. |
| Installation & Cost | Simple installation; most cost-effective when reinforcement is needed mainly in one direction. | Easy installation over large areas; moderate cost and fast construction speed. | Higher material cost and specification control; justified by performance gains in demanding projects. |
| Typical Engineering Applications |
|
|
|
| Recommended Use | Use when the design requires high reinforcement in a single direction and maximum wall/slope stability. | Choose for large-area subgrade where two-axis load sharing and settlement control are critical. | Specify for complex loading, turning traffic, and projects demanding the highest multi-axial stability. |
In summary: Uniaxial geogrid delivers strong reinforcement in one direction for walls and steep slopes; Biaxial geogrid balances strength in two directions for roads and large-area foundations; Triaxial/Multiaxial geogrid provides the best multi-directional load distribution for airports, container yards and other heavy-duty pavements.
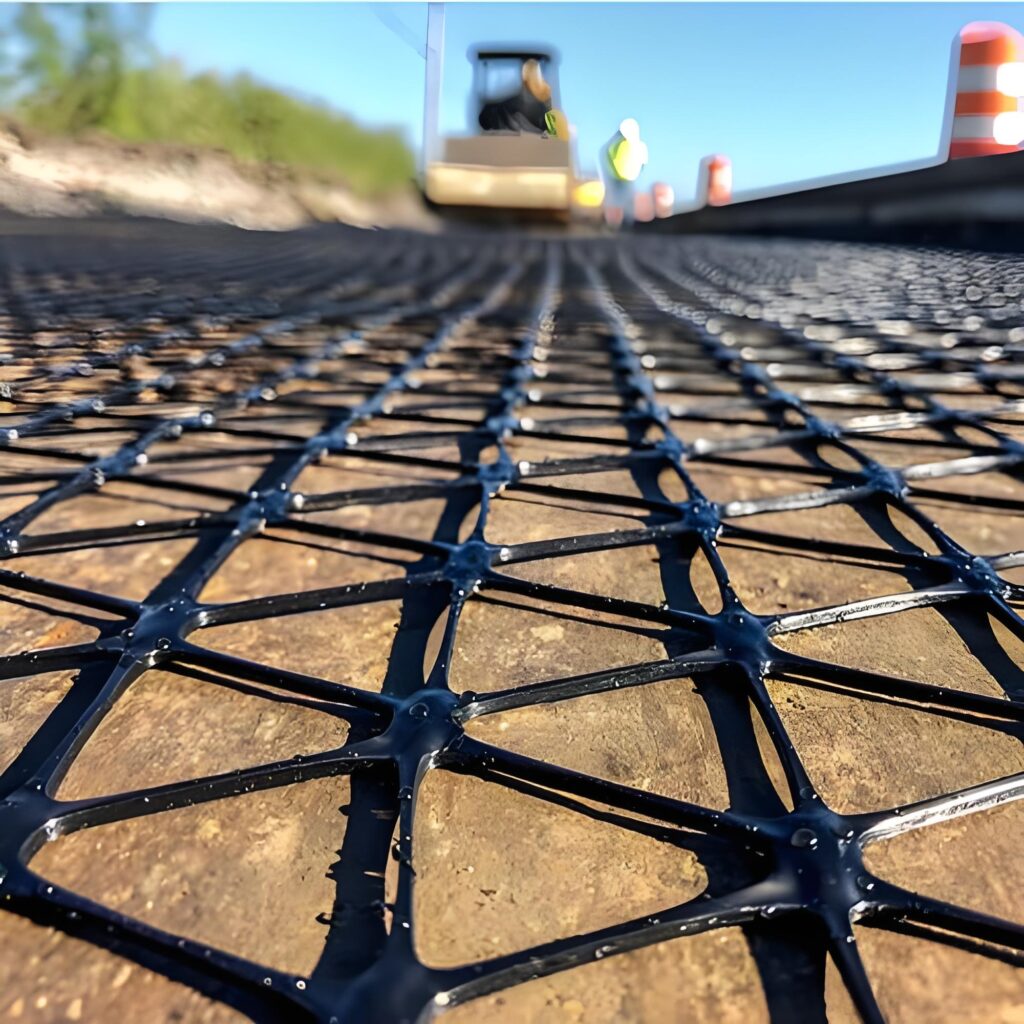

Tweeassige Geogrid Installation&Quality Control (CQA)
Laying Methods
Oppervlakvoorbereiding:
Ensure the foundation surface is level, well-compacted, and free from sharp debris or standing water that could damage the geogrid. Verify the design elevation and alignment before installation to maintain surface uniformity and contact between soil and geogrid. A stable, firm base helps achieve uniform load transfer across both directions.
Unrolling & Orientation:
Biaxial geogrids are delivered in rolls and can be unrolled manually or by light machinery along the prepared surface.
Unlike uniaxial types, biaxial geogrids can be laid in any direction, as they have equal tensile strength in both longitudinal and transverse axes. Ensure the sheets are straight, flat, and free from folds or tension waves during placement.
Overlap Width:
For effective interlocking and load transfer, overlap adjacent sheets by 200–400 mm on both sides.
In areas with weak subgrades or heavy traffic loads, an overlap of up to 500 mm is recommended.
Secure overlaps with U-shaped pins, plastic ties, or staples at intervals of 1.0–1.5 m to prevent shifting during filling and compaction.
Backfilling & Kompaksie:
Spread the fill material gently over the geogrid from one end to the other, avoiding direct dumping from trucks to prevent displacement or damage.
Compact the fill in thin layers of 150–200 mm, using lightweight rollers or plate compactors. Proper compaction ensures full interlock between the aggregate and geogrid ribs, improving reinforcement performance and reducing settlement.
Anchorage at Edges:
At the edges or terminations, anchor the geogrid securely using pegs, sandbags, or mechanical fasteners before placing the next layer of fill. Ensure all corners and boundaries maintain firm contact with the subgrade to avoid curling or movement.
CQA Recommendations
Confirm that the tensile strength and aperture dimensions comply with the design specifications (e.g., GB/T 17689 or ASTM D6637).
Inspect each roll before use for tears, cuts, or chemical contamination.
Verify overlap width, anchorage spacing, and installation direction are consistent across the site.
Record batch numbers, installation area, date, and weather conditions for each section in the CQA log.
Ensure backfill material meets grading and compaction requirements to maintain interlock efficiency.
Avoid any construction vehicle movement on uncovered geogrid sections.
Hoekom kies WP Spesialis?
Oor die jare, WP Spesialis has established itself as one of China’s reliable Biaxial geogrid manufacturers and trusted suppliers of geosynthetic reinforcement materials for global infrastructure projects.
We specialize in producing high-performance PP and HDPE uniaxial geogrids designed to improve soil stability, load-bearing capacity, and long-term performance in retaining walls, slopes, embankments, and road foundations.
Our geogrids deliver exceptional tensile strength, creep resistance, and durability — supported by factory-direct supply, professional technical guidance, and strict quality control.
- Free Samples of Biaxial Geogrid
- Kundige projekondersteuning
- Betroubare kwaliteitsversekering
- Meer as 10 jaar se vervaardigingservaring
- Fabrieks direkte voorsiening
Ready to Specify a Geogrid?
- 15+ jaar van fabriek-direkte kundigheid
- Aangepaste ontwerpte oplossings vir u behoeftes
- Globale aflewering & Logistieke ondersteuning
- 'N deursigtige kwotasie sonder verpligting
- 100% vertroulikheid gewaarborg
Jou e-posinligting sal streng vertroulik gehou word en ons besigheidspersoneel sal verseker dat jou privaat inligting absoluut veilig is!
Kontak
- info@waterproofspecialist.com
Antwoord binne 12 uur!
Let asseblief op die e -pos met die agtervoegsel “@WaterProofspecialist.com”.


